AWS Mastery: 7 Ultimate Secrets to Dominate Cloud Computing
Cloud computing isn’t just the future—it’s the present. And at the heart of this revolution stands AWS, the undisputed leader in cloud infrastructure. Let’s dive into what makes Amazon Web Services so powerful and how you can harness its full potential.
What Is AWS and Why It Dominates the Cloud

Amazon Web Services (AWS) is more than just a cloud platform—it’s a global ecosystem powering millions of businesses, startups, and governments. Launched in 2006, AWS was the first major player to offer scalable, on-demand cloud computing resources, and it hasn’t looked back since.
The Birth of AWS: A Game-Changing Vision
AWS emerged from Amazon’s internal need to manage its massive e-commerce infrastructure. Engineers realized that the scalable, modular systems they built could be offered as services to others. This insight led to the launch of core services like Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) and EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud).
- Amazon S3 launched in 2006, offering reliable, scalable object storage.
- Amazon EC2 followed shortly after, enabling users to rent virtual servers in the cloud.
- These foundational services laid the groundwork for the modern cloud economy.
The decision to externalize Amazon’s internal tools was revolutionary. As AWS officially states, the goal was to provide businesses with the same infrastructure advantages that Amazon enjoyed—without the upfront capital investment.
Market Leadership and Global Reach
Today, AWS holds over 30% of the global cloud infrastructure market, far ahead of competitors like Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. Its dominance isn’t accidental—it’s built on unmatched scale, innovation, and reliability.
- Operates in 33 geographic regions worldwide, with 102 Availability Zones (as of 2024).
- Serves customers in over 240 countries and territories.
- Supports critical workloads for companies like Netflix, Airbnb, and the U.S. Department of Defense.
“AWS has set the standard for cloud computing. Its breadth and depth of services are unmatched.” — Gartner, 2023 Cloud Infrastructure Report
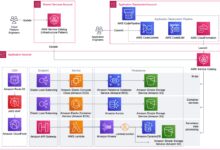
Core AWS Services Every Developer Should Know
To truly understand AWS, you need to explore its core service categories. These form the backbone of nearly every cloud deployment and are essential knowledge for developers, architects, and IT professionals.
Compute: Powering Your Applications
AWS offers multiple compute options tailored to different use cases. The most widely used is Amazon EC2, which allows users to launch virtual machines in minutes.
- EC2 instances come in various types (e.g., general purpose, memory optimized, GPU accelerated).
- Users can scale up or down based on demand using Auto Scaling groups.
- Pricing models include On-Demand, Reserved Instances, and Spot Instances for cost savings.
Another key compute service is AWS Lambda, a serverless offering that runs code in response to events without requiring server management. This is ideal for microservices, data processing, and automation tasks.
Storage: Secure, Scalable, and Global
AWS provides a range of storage solutions, each designed for specific performance, durability, and cost requirements.
- Amazon S3 is the go-to for object storage, offering 99.999999999% durability.
- Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) provides block-level storage for EC2 instances.
- Amazon Glacier is optimized for long-term archival and backup with low-cost storage tiers.
These services integrate seamlessly with other AWS tools, enabling automated lifecycle policies, cross-region replication, and encryption by default.
Networking & Content Delivery
AWS networking services ensure secure, high-performance connectivity across your cloud environment.
- Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) lets you define isolated virtual networks.
- AWS Direct Connect provides private network connections from on-premises to AWS.
- Amazon CloudFront is a global content delivery network (CDN) that accelerates website and app performance.
Together, these services enable enterprises to build hybrid architectures, enforce strict security policies, and deliver content with minimal latency.
How AWS Transforms Business Operations
Organizations of all sizes leverage AWS to innovate faster, reduce costs, and improve agility. The platform’s flexibility allows businesses to experiment, scale, and respond to market changes in real time.
Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go Model
One of the biggest advantages of AWS is its pricing model. Unlike traditional IT infrastructure, which requires large capital expenditures (CapEx), AWS operates on an operational expenditure (OpEx) model.
- No upfront hardware costs—pay only for what you use.
- Flexible pricing options like Reserved Instances can reduce costs by up to 75%.
- Tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Trusted Advisor help monitor and optimize spending.
This shift enables startups to launch with minimal investment and allows enterprises to reallocate budgets toward innovation rather than maintenance.
Scalability and Elasticity
AWS allows businesses to scale resources up or down automatically based on demand. This elasticity is crucial for handling traffic spikes, seasonal trends, or unexpected growth.
- Auto Scaling adjusts the number of EC2 instances in real time.
- Elastic Load Balancing distributes traffic across healthy instances.
- Serverless architectures (e.g., Lambda + API Gateway) scale to zero when idle, reducing costs.
For example, a retail company can handle Black Friday traffic seamlessly by leveraging AWS’s auto-scaling capabilities, then scale back down afterward—something nearly impossible with on-premises infrastructure.
Innovation at Speed
AWS empowers organizations to innovate rapidly by removing infrastructure bottlenecks.
- Developers can spin up environments in minutes using Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like AWS CloudFormation or Terraform.
- Integrated CI/CD pipelines via AWS CodePipeline and CodeBuild accelerate software delivery.
- Access to cutting-edge technologies like AI/ML (via SageMaker), IoT, and blockchain lowers the barrier to entry.
This agility allows companies to test new ideas quickly, fail fast, and iterate—key principles in today’s competitive landscape.
Security and Compliance in AWS
Security is a top concern for any organization moving to the cloud. AWS addresses this through a shared responsibility model and a comprehensive suite of security tools.
Shared Responsibility Model Explained
In AWS’s shared responsibility model, security responsibilities are divided between AWS and the customer.
- AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud (e.g., physical data centers, hardware, hypervisors).
- Customers are responsible for security in the cloud (e.g., IAM policies, data encryption, OS patching).
- This model ensures clarity and accountability on both sides.
Understanding this distinction is critical to building secure architectures. Misconfigurations by customers remain the leading cause of cloud breaches.
Key Security Services and Best Practices
AWS offers a robust set of tools to help customers secure their environments.
- Amazon GuardDuty provides intelligent threat detection using machine learning.
- AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) enables fine-grained access control.
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS) simplifies encryption key management.
Best practices include enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA), using least-privilege permissions, and regularly auditing configurations with AWS Config.
Compliance and Certifications
AWS complies with a wide range of global and industry-specific standards, making it suitable for regulated industries.
- Compliance programs include GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOC 1/2/3, and ISO 27001.
- AWS Artifact provides on-demand access to compliance reports and agreements.
- Region-specific compliance ensures data residency requirements are met.
This extensive compliance portfolio allows financial institutions, healthcare providers, and government agencies to confidently adopt AWS.
AWS vs. Competitors: Why It Stands Out
While Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform are strong contenders, AWS maintains a significant edge in several key areas.
Breadth and Depth of Services
AWS offers over 200 fully featured services across compute, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, and more. No other provider comes close in terms of service variety.
- Specialized services like AWS Outposts bring AWS infrastructure on-premises.
- Industry-specific solutions for healthcare (AWS HealthLake), finance, and media.
- Continuous innovation with dozens of new services launched annually.
This breadth allows AWS to support virtually any workload, from legacy applications to cutting-edge AI research.
Global Infrastructure and Reliability
AWS’s global footprint is unmatched. With more Regions and Availability Zones than any competitor, it offers superior redundancy and low-latency access worldwide.
- Each Region is isolated for fault tolerance.
- Availability Zones are physically separate data centers within a Region.
- This architecture enables high availability and disaster recovery strategies.
For global enterprises, this means they can deploy applications closer to users, improving performance and compliance.
Ecosystem and Partner Network
AWS has cultivated the largest ecosystem of partners, consultants, and third-party tools.
- The AWS Partner Network (APN) includes thousands of consulting and technology partners.
- Marketplaces for software, data, and services simplify procurement.
- Strong developer community with extensive documentation, forums, and training.
This ecosystem reduces implementation time and provides access to expert support when needed.
Getting Started with AWS: A Step-by-Step Guide
Starting with AWS can feel overwhelming, but with the right approach, you can quickly get up and running.
Create an AWS Account and Set Up Billing Alerts
The first step is creating an AWS account at aws.amazon.com. During signup, you’ll provide billing information and verify your identity.
- Use a strong password and enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) immediately.
- Set up billing alerts using Amazon CloudWatch to avoid unexpected charges.
- Take advantage of the AWS Free Tier, which includes 12 months of free services and always-free offerings.
These steps ensure a secure and cost-controlled onboarding experience.
Explore the AWS Management Console
The AWS Management Console is a web-based interface for managing all AWS services.
- It provides a dashboard view of your resources, usage, and costs.
- Services are organized by category (e.g., Compute, Storage, Database).
- You can search for services, launch resources, and monitor performance.
Familiarizing yourself with the console is essential for day-to-day operations.
Launch Your First EC2 Instance
Launching an EC2 instance is a great way to experience AWS firsthand.
- Navigate to the EC2 dashboard and click “Launch Instance”.
- Choose an Amazon Machine Image (AMI), such as Amazon Linux 2.
- Select an instance type (e.g., t2.micro, eligible for Free Tier).
- Configure security groups to allow SSH or HTTP access.
- Review and launch, using a key pair for secure login.
Within minutes, you’ll have a running virtual server in the cloud—ready for experimentation.
Advanced AWS Strategies for Enterprises
For large organizations, AWS offers advanced capabilities to manage complexity, ensure governance, and drive digital transformation.
Multi-Account Architecture and AWS Organizations
Enterprises often use multiple AWS accounts to separate environments (e.g., development, staging, production) and enforce security boundaries.
- AWS Organizations enables centralized management of multiple accounts.
- You can apply Service Control Policies (SCPs) to restrict actions across accounts.
- Consolidated billing simplifies cost tracking and payment.
This structure improves security, compliance, and operational efficiency.
Infrastructure as Code with AWS CloudFormation
Managing infrastructure manually doesn’t scale. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) allows you to define and deploy resources programmatically.
- AWS CloudFormation uses JSON or YAML templates to model your infrastructure.
- Templates can be version-controlled, reviewed, and reused.
- Changes are applied in a predictable, auditable manner.
This approach reduces human error and accelerates deployment cycles.
Monitoring and Observability with AWS CloudWatch
To maintain performance and reliability, enterprises need deep visibility into their systems.
- AWS CloudWatch collects metrics, logs, and events from AWS resources.
- You can set alarms, create dashboards, and trigger automated responses.
- Integration with AWS X-Ray enables distributed tracing for microservices.
Together, these tools provide comprehensive observability across complex architectures.
The Future of AWS: Trends and Innovations
AWS continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible in cloud computing. Several emerging trends highlight its strategic direction.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
AWS is democratizing access to artificial intelligence through services like Amazon SageMaker.
- SageMaker enables developers to build, train, and deploy ML models at scale.
- Pre-built AI services (e.g., Rekognition, Transcribe, Comprehend) require no ML expertise.
- Integration with data lakes and analytics tools streamlines AI workflows.
These capabilities are transforming industries from healthcare to retail.
Edge Computing with AWS Wavelength and Outposts
To support low-latency applications like AR/VR, autonomous vehicles, and IoT, AWS is extending its reach to the edge.
- AWS Wavelength embeds AWS compute and storage within 5G networks.
- AWS Outposts brings native AWS services into on-premises data centers.
- This hybrid approach meets performance and regulatory requirements.
Edge computing ensures data is processed closer to the source, reducing latency and bandwidth costs.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Initiatives
AWS is committed to sustainability, aiming to power its operations with 100% renewable energy by 2025.
- Investments in wind and solar farms across the globe.
- Energy-efficient data center designs reduce power usage.
- Tools like the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool help customers track emissions.
This focus on sustainability aligns with global climate goals and corporate ESG initiatives.
What is AWS and why is it important?
AWS (Amazon Web Services) is the world’s most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform. It’s important because it enables businesses to innovate faster, scale on demand, and reduce IT costs by eliminating the need for physical data centers.
Is AWS free to use?
AWS offers a Free Tier that includes limited access to many services for 12 months, plus always-free usage tiers for services like Lambda and S3. However, most production workloads incur costs based on usage.
How does AWS compare to Azure and Google Cloud?
AWS leads in market share, service breadth, and global infrastructure. While Azure excels in Microsoft ecosystem integration and Google Cloud in data analytics and AI, AWS offers the most mature and extensive cloud platform overall.
What are the most popular AWS services?
The most popular AWS services include Amazon EC2 (compute), S3 (storage), Lambda (serverless), RDS (databases), CloudFront (CDN), and IAM (security). These form the foundation of most cloud architectures.
How can I learn AWS?
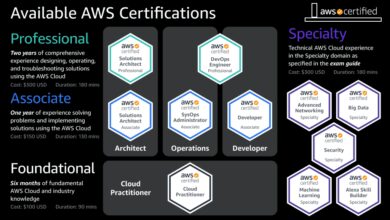
You can learn AWS through official resources like AWS Training and Certification, hands-on labs, free tier experimentation, and third-party platforms like A Cloud Guru or Coursera. Starting with the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner is a great entry point.
Amazon Web Services has redefined how businesses think about technology. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, AWS provides the tools, scalability, and innovation needed to thrive in the digital age. Whether you’re launching your first server or building a global AI platform, AWS offers the foundation to succeed. The future of computing is in the cloud—and AWS is leading the charge.
Further Reading: