AWS Glue: 7 Powerful Reasons to Transform Your Data Workflow
Imagine automating your entire data integration process without writing a single line of code. With AWS Glue, that’s not just possible—it’s seamless. This fully managed ETL service is revolutionizing how businesses handle data across cloud environments.
What Is AWS Glue and Why It Matters

AWS Glue is a fully managed extract, transform, and load (ETL) service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It simplifies the process of preparing and loading data for analytics, making it a cornerstone for modern data-driven organizations. Whether you’re dealing with structured or unstructured data, AWS Glue automates the heavy lifting involved in data integration.
Core Components of AWS Glue
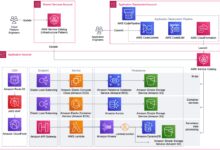
Understanding the architecture of AWS Glue is essential to leveraging its full potential. The service is built on several interconnected components that work together to streamline ETL workflows.
Glue Data Catalog: Acts as a persistent metadata store, similar to Apache Hive’s metastore.It stores table definitions, schemas, and partition information.Glue Crawlers: Automatically scan data sources to infer schemas and populate the Data Catalog with metadata.Glue ETL Jobs: Run scripts (Python or Scala) to transform and move data between sources and targets.”AWS Glue eliminates the need for manual schema discovery and job scripting, reducing time-to-insight from weeks to hours.” — AWS Official DocumentationHow AWS Glue Fits into the AWS EcosystemAWS Glue integrates natively with other AWS services such as Amazon S3, Redshift, RDS, and Athena..
This tight integration allows for end-to-end data pipelines within the AWS cloud.For example, you can use Glue to extract data from S3, transform it using PySpark, and load it into Amazon Redshift for business intelligence reporting..
Its compatibility with AWS Glue Studio also enables visual job creation, making it accessible even to users with limited programming experience. This synergy enhances data governance, security, and operational efficiency across the platform.
Key Features That Make AWS Glue Stand Out
AWS Glue offers a suite of powerful features designed to simplify data integration at scale. These features are engineered to reduce complexity while maximizing performance and flexibility in ETL operations.
Serverless Architecture and Auto-Scaling
One of the most compelling aspects of AWS Glue is its serverless nature. You don’t need to provision or manage servers. When you run a Glue job, AWS automatically allocates the necessary compute resources (known as Dynamic Executors) and scales them based on workload demands.
This auto-scaling capability ensures optimal resource utilization and cost efficiency. You only pay for the compute time consumed during job execution, measured in Glue Units (GUs), which include memory, vCPU, and storage.
Intelligent Schema Discovery with Crawlers
Data comes in many formats—CSV, JSON, Parquet, ORC, and more. Manually defining schemas for each dataset is time-consuming and error-prone. AWS Glue Crawlers solve this problem by automatically scanning data stores and inferring schema structures.
Crawlers support various data sources including Amazon S3, JDBC databases, MongoDB, and Kafka. Once a crawler runs, it updates the Glue Data Catalog with table definitions, data types, and partition keys. This metadata becomes the foundation for ETL jobs and querying via Athena or Redshift Spectrum.
Code Generation and Visual ETL with Glue Studio
Not everyone is a developer, but that shouldn’t be a barrier to building ETL pipelines. AWS Glue Studio provides a drag-and-drop interface for creating ETL jobs without writing code.
Behind the scenes, Glue Studio generates Python or Scala scripts using PySpark or Spark SQL. These scripts can be further customized if needed. This hybrid approach—visual design with optional code editing—empowers both technical and non-technical users to participate in data engineering workflows.
Deep Dive into AWS Glue ETL Jobs
At the heart of AWS Glue are ETL jobs—automated workflows that extract data, apply transformations, and load results into target destinations. These jobs are where the real magic happens in data integration.
Creating and Running ETL Jobs
To create an ETL job in AWS Glue, you start by selecting a data source (e.g., an S3 bucket or RDS instance) and a target (like Redshift or another S3 location). Glue then generates a script template using either Python (PySpark) or Scala (Spark).
You can edit the script directly in the AWS console or using AWS Glue Studio. Once configured, the job can be triggered manually, scheduled via cron expressions, or initiated by events (e.g., new files arriving in S3 via Amazon EventBridge).
Using PySpark and Spark SQL in Glue Jobs
AWS Glue is built on Apache Spark, one of the most powerful open-source data processing engines. This means you can leverage PySpark and Spark SQL to perform complex transformations like filtering, joining, aggregating, and cleansing data.
For example, you might write a PySpark transformation to clean customer data by removing duplicates, standardizing addresses, and enriching records with geolocation data. Glue provides a development endpoint and Jupyter notebooks for testing and debugging these scripts before deployment.
“Glue’s integration with Spark gives data engineers the power of distributed computing without managing clusters.” — AWS Big Data Blog
AWS Glue Data Catalog: The Heart of Metadata Management
The AWS Glue Data Catalog is more than just a schema repository—it’s a central metadata management system that enables discoverability, governance, and reuse across your organization.
How the Data Catalog Works
When a Glue crawler runs, it connects to a data store, reads sample files, and infers the schema. It then creates or updates a table in the Data Catalog, storing metadata such as column names, data types, location, and classification (e.g., CSV, JSON).
This catalog is searchable and can be accessed by multiple AWS services. For instance, Amazon Athena uses the Glue Data Catalog to execute SQL queries directly on S3 data, eliminating the need to load data into a database first.
Integration with AWS Lake Formation
For organizations requiring fine-grained access control and data governance, AWS Glue integrates seamlessly with AWS Lake Formation. Lake Formation allows you to define table-level and column-level permissions, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
By combining Glue’s metadata capabilities with Lake Formation’s security model, enterprises can build secure, governed data lakes on Amazon S3. This integration is critical for large-scale analytics initiatives where data lineage and access auditing are mandatory.
Serverless Options: AWS Glue vs Glue Elastic Views
While traditional Glue jobs are ideal for batch processing, AWS has introduced newer serverless options to address real-time and materialized view use cases.
Understanding Glue Elastic Views
AWS Glue Elastic Views allows you to create materialized views that combine and replicate data from multiple sources into a target database or data warehouse. Unlike traditional ETL jobs, Elastic Views continuously update the target as source data changes—making it perfect for near-real-time analytics.
For example, you could use Elastic Views to merge customer data from Amazon DynamoDB with order history from RDS and serve it to Amazon Redshift for live dashboards. The service handles all the underlying change data capture (CDC) and incremental updates automatically.
When to Use Glue Jobs vs Elastic Views
Choosing between Glue ETL jobs and Elastic Views depends on your use case:
- Use Glue ETL Jobs: For scheduled batch processing, complex transformations, data cleansing, and one-time migrations.
- Use Glue Elastic Views: For continuous data replication, real-time dashboards, and simplifying access to fragmented data sources.
Both options are serverless and integrate with the Glue Data Catalog, ensuring consistency in metadata and governance.
Performance Optimization and Cost Management in AWS Glue
While AWS Glue offers ease of use, optimizing performance and controlling costs require strategic planning and monitoring.
Tuning Glue Job Performance
Several factors influence the performance of Glue jobs, including the number of workers (executors), job bookmarks, and partitioning strategies.
- Job Bookmarks: Enable Glue to track processed data and avoid reprocessing the same files, improving efficiency for incremental loads.
- Partitioning: Organizing data in S3 by date, region, or category helps Glue read only relevant partitions, reducing I/O and runtime.
- Worker Types: Choose between Standard, G.1X, and G.2X workers based on memory and compute needs. G.2X is ideal for memory-intensive transformations.
Additionally, enabling Spark UI and CloudWatch Logs allows you to monitor job execution, identify bottlenecks, and optimize scripts accordingly.
Cost-Saving Strategies
Since AWS Glue charges based on Glue Units (GUs) consumed per second, minimizing job duration is key to cost control.
- Use Auto-Scaling: Let AWS dynamically adjust the number of executors based on workload.
- Optimize Script Logic: Avoid full table scans; use filters and projections early in the transformation pipeline.
- Leverage Spot Instances: For fault-tolerant jobs, use spot pricing to reduce costs by up to 70%.
Regularly reviewing job metrics in CloudWatch and setting up billing alerts can prevent unexpected charges.
Real-World Use Cases of AWS Glue
AWS Glue is not just a theoretical tool—it’s being used by companies across industries to solve real data challenges.
Data Lake Ingestion and Preparation
Many organizations use AWS Glue to build and maintain data lakes on Amazon S3. For example, a retail company might ingest sales data from multiple stores in various formats (CSV, JSON) into S3.
Glue crawlers automatically detect new files, infer schemas, and catalog them. ETL jobs then transform the raw data into a standardized format (e.g., Parquet), partition it by date, and load it into a curated zone for analytics. This process enables fast, scalable querying using Athena or Redshift.
Database Migration and Modernization
When migrating from on-premises databases to the cloud, AWS Glue plays a crucial role. A financial institution moving from Oracle to Amazon Redshift can use Glue to extract data, transform legacy formats, and load it into the new warehouse.
Glue supports JDBC connectors for most relational databases, making it easy to integrate with existing systems. The service also handles data type mapping and schema conversion, reducing manual effort and errors.
Streaming Data Integration with Glue Streaming
For real-time data processing, AWS Glue supports streaming ETL jobs that consume data from Amazon Kinesis and MSK (Managed Streaming for Kafka).
A media company might use Glue streaming jobs to process user engagement data (clicks, views, watch time) in real time, enrich it with user profiles, and load it into Amazon Elasticsearch for live monitoring. This enables immediate insights and rapid response to user behavior trends.
Security, Compliance, and Governance in AWS Glue
In enterprise environments, security and compliance are non-negotiable. AWS Glue provides robust mechanisms to protect data and ensure regulatory adherence.
Encryption and IAM Policies
All data processed by AWS Glue can be encrypted at rest and in transit. You can enable AWS KMS (Key Management Service) to manage encryption keys and control access.
Additionally, IAM roles and policies define who can create, modify, or run Glue jobs. For example, you can restrict developers to read-only access on production catalogs while allowing admins full control.
Audit Logging and Data Lineage
With AWS CloudTrail and Glue’s built-in logging, every action in the Glue environment is tracked. This includes crawler runs, job executions, and catalog modifications.
Data lineage—tracking how data flows from source to destination—is supported through integration with AWS Lake Formation and third-party tools. This transparency is essential for audits and troubleshooting.
What is AWS Glue used for?
AWS Glue is primarily used for automating ETL (extract, transform, load) processes. It helps organizations prepare and load data for analytics by discovering, cleaning, enriching, and moving data between various sources and targets like S3, Redshift, and RDS.
Is AWS Glue serverless?
Yes, AWS Glue is a fully serverless service. It automatically provisions and scales the necessary compute resources for ETL jobs, so you don’t need to manage servers or clusters. You only pay for the resources used during job execution.
How much does AWS Glue cost?
AWS Glue pricing is based on the number of Data Catalog objects, crawler runtime, and ETL job runtime measured in Glue Units (GUs). Costs vary depending on usage, but you can use the AWS Pricing Calculator to estimate expenses based on your workload.
Can AWS Glue handle real-time data?
Yes, AWS Glue supports streaming ETL jobs that process data from Amazon Kinesis and MSK (Managed Streaming for Kafka) in near real time. This allows for real-time data transformation and loading into analytics systems.
How does AWS Glue compare to Apache Airflow?
AWS Glue is focused on ETL automation and schema discovery, while Apache Airflow (available on AWS via MWAA) is a workflow orchestration tool. Glue can be used within Airflow DAGs, but they serve different primary purposes: Glue for data transformation, Airflow for pipeline orchestration.
AWS Glue is a transformative tool in the modern data stack. By automating ETL, providing intelligent schema discovery, and offering seamless integration with the AWS ecosystem, it empowers organizations to unlock the value of their data faster and more efficiently. Whether you’re building a data lake, migrating databases, or processing streaming data, AWS Glue provides the scalability, security, and simplicity needed to succeed in today’s data-driven world.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: